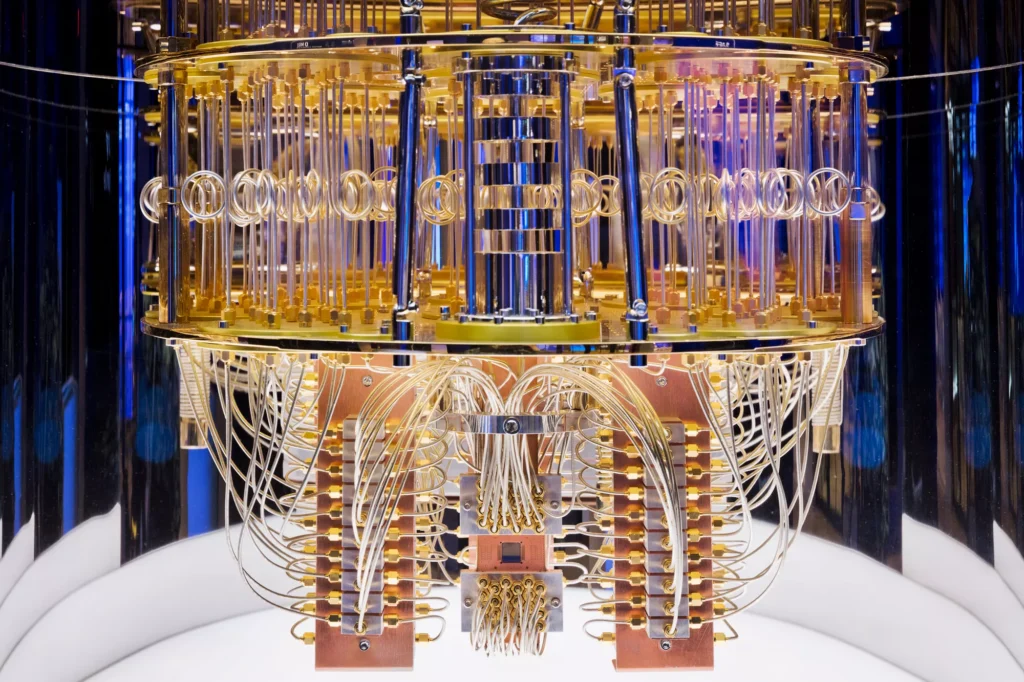
In the world of computing, quantum computers represent the next frontier, promising to solve problems far beyond the reach of classical machines. While traditional computers have powered innovation for decades, quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize industries by unlocking immense processing power and delivering solutions to problems that are currently unsolvable. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating world of quantum computing, exploring its underlying principles, current advancements, and future implications.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics—the fundamental theory in physics that describes the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as the smallest unit of data, quantum computers use qubits (quantum bits) to encode information.
A classical bit can be in one of two states: 0 or 1. In contrast, a qubit can be in a state of 0, 1, or any quantum superposition of these states. This means that a quantum computer, with multiple qubits, can process exponentially more information than a classical computer.
Key Principles of Quantum Computing
- Superposition
Superposition allows a quantum computer to represent multiple states simultaneously. In a classical system, a bit is either 0 or 1, but a qubit can be both 0 and 1 at the same time, thanks to superposition. This unique capability exponentially increases the computing power and enables quantum computers to process vast amounts of data simultaneously. - Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more qubits become linked, meaning the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of the other, no matter the distance between them. This interconnectedness allows quantum computers to perform computations at speeds unattainable by classical machines. - Quantum Interference
Quantum interference occurs when quantum states are manipulated to influence the probability of certain outcomes. By adjusting the interference, quantum computers can steer their calculations toward the most likely correct answers, improving the accuracy and speed of problem-solving.
How Does a Quantum Computer Work?
A quantum computer consists of several qubits that form the foundation for processing quantum information. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how quantum computing works:
- Initialization
Quantum computers start by initializing the qubits in a known state, such as 0. This is the quantum equivalent of a classical computer’s startup. - Superposition & Entanglement
Qubits are then placed into a superposition, where they can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously. Quantum gates manipulate these qubits, causing them to interact in ways that create entanglement, which exponentially increases computational capacity. - Quantum Gates
Quantum gates manipulate qubits to change their states. Unlike classical gates (AND, OR, NOT), quantum gates are reversible and are used to apply specific quantum operations, such as changing probabilities or manipulating superposition. - Measurement
After the quantum computation process, the qubits are measured. Upon measurement, the superposition collapses into a specific classical state (either 0 or 1), and the result is interpreted based on the probabilities of different outcomes.
Advantages of Quantum Computing
- Solving Complex Problems Faster
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems—like optimization issues, molecular simulations, and cryptographic algorithms—much faster than classical computers. These capabilities are especially relevant for fields such as drug discovery, financial modeling, and materials science, where traditional computers struggle to process the enormous amounts of data. - Encryption and Security
Quantum computing has significant implications for encryption and cybersecurity. While it poses a challenge to existing encryption algorithms (like RSA) by potentially cracking them, it also offers new encryption methods based on quantum principles, such as quantum cryptography. - Optimization
Quantum computing excels in optimization problems, which are often difficult for classical computers. It can evaluate multiple solutions at once and provide the most efficient option, making it invaluable for industries such as logistics, supply chain management, and artificial intelligence. - Parallelism
Quantum computers can perform multiple calculations simultaneously due to the superposition principle. This makes quantum systems much faster at tasks like searching unsorted databases, analyzing large datasets, or solving large-scale problems that require massive computational resources.
Applications of Quantum Computing
- Drug Discovery and Healthcare
Quantum computers could model molecular structures and chemical reactions at a granular level, speeding up the process of drug discovery and development. Simulating molecular interactions on a quantum level can help researchers design better drugs and treatments for complex diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and more. - Cryptography and Data Security
As quantum computing progresses, traditional cryptographic methods may become vulnerable to attack. Quantum algorithms like Shor’s algorithm can efficiently factor large numbers, which is the basis of most encryption systems today. However, quantum cryptography offers new ways to secure data, such as Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that any attempt to intercept communication can be detected. - Financial Modeling
The financial industry deals with a massive number of variables and complex systems that can be challenging to model using classical computers. Quantum computers can analyze and predict market behavior more effectively, allowing for better risk analysis, optimization of investment portfolios, and identification of new market opportunities. - Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning benefit from the high computational power of quantum computers, especially in terms of training models and processing large datasets. Quantum algorithms can speed up machine learning processes, improving the efficiency and accuracy of AI applications. - Material Science
Quantum computers can simulate and model the properties of materials at an atomic level. This ability has the potential to accelerate the discovery of new materials for a variety of applications, including renewable energy technologies, semiconductors, and superconductors.
Challenges Facing Quantum Computing
Despite its promising potential, quantum computing is still in its infancy, and several challenges remain before it becomes mainstream:
- Qubit Stability (Decoherence)
Quantum systems are extremely sensitive to environmental factors like temperature and electromagnetic fields. This leads to a phenomenon called decoherence, where qubits lose their quantum state, causing errors in calculations. Researchers are working on improving qubit stability and developing error correction techniques to overcome this challenge. - Scaling Up
Currently, quantum computers are limited in the number of qubits they can process. As quantum computers scale, maintaining coherence across many qubits becomes exponentially more difficult. Building quantum computers with thousands or millions of qubits will require significant technological advancements. - High Costs
Quantum computers are extremely expensive to build and maintain. The infrastructure requires highly controlled environments, including cryogenic temperatures, to stabilize qubits. This makes quantum computing research and development accessible to only a few organizations and institutions around the world. - Software Development
Programming quantum computers is vastly different from traditional programming. Developers need to learn how to code quantum algorithms, which requires specialized knowledge in quantum mechanics and mathematics. Creating accessible and user-friendly quantum software is another hurdle for widespread adoption.
The Future of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is expected to revolutionize industries by solving problems that were once considered unsolvable. As technology advances, we may see quantum computers becoming more accessible, affordable, and powerful. Major tech companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft are making significant strides in developing quantum computing systems, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
While quantum computing is not yet ready for everyday use, its development has the potential to transform fields ranging from science and healthcare to finance and cybersecurity. The continued research in quantum algorithms, qubit stability, and error correction will be critical to unlocking its full potential.
Conclusion
Quantum computing represents a monumental leap in the field of computation, offering capabilities far beyond the reach of classical computers. Though still in its early stages, its potential to revolutionize industries is clear, with applications in areas like cryptography, artificial intelligence, drug discovery, and financial modeling. The ability to solve complex problems faster, optimize processes, and enhance security makes quantum computing one of the most exciting advancements in modern technology.
As quantum computers evolve and overcome current challenges, they may soon become a vital tool for scientists, researchers, and businesses, shaping the future of computing and technological progress.
If you want to stay updated on cutting-edge technology like quantum computing, visit Techstertech.com for more insights and expert solutions tailored to your business needs.